From 2D to 4D: How AI-Driven 4D Maps Are Changing the World
Maps have traditionally served as static representations of our world, capturing a specific moment in time. However, with advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), we’re witnessing the evolution of maps from two-dimensional (2D) snapshots to dynamic four-dimensional (4D) tools that incorporate the dimension of time. These AI-driven 4D maps not only depict geographical spaces but also illustrate how landscapes and urban environments transform over periods, offering a comprehensive view of change and progression.
The Evolution from 2D to 4D Mapping
Historically, maps have been invaluable for navigation and understanding spatial relationships. Yet, they could not convey temporal changes. The integration of AI has revolutionized this aspect by enabling the creation of 4D maps that visualize changes over time. This transformation is achieved through the analysis of vast datasets, including satellite imagery, sensor data, and historical records, allowing AI to model and predict temporal shifts in various environments.
What Makes AI-driven 4D Maps Different?
A traditional map provides a fixed representation of geographic data, while a 3D map adds depth, enabling better visualization of landscapes and structures. A 4D map, on the other hand, introduces time as a critical factor. This means that users can see past changes, monitor present conditions, and even predict future developments.
Imagine a 4D map of a growing city—one that allows urban planners to observe how new infrastructure affects traffic patterns, green spaces, and population density over decades. Or consider a climate-focused 4D map that tracks the melting of glaciers over time, offering insights into the long-term effects of global warming.
The Role of AI in 4D Mapping
AI is the backbone of modern 4D mapping technology. By processing vast datasets from satellites, drones, IoT sensors, and historical archives, AI can detect patterns and predict future developments with remarkable accuracy. Some of the key AI-driven technologies powering 4D maps include:
Machine Learning & Pattern Recognition
AI algorithms analyze historical and real-time data to identify patterns in how landscapes and cities evolve. For instance, machine learning models can predict how an urban area will expand based on past construction trends and economic factors. These insights are crucial for city planners and developers looking to optimize land use.
Remote Sensing & Satellite Imagery
Satellites capture real-time images of the Earth’s surface, and AI processes these images to detect subtle changes over time. Whether monitoring deforestation in the Amazon rainforest or tracking coastal erosion, 4D maps powered by satellite data help scientists and policymakers make informed decisions.
Digital Twins
A digital twin is a virtual replica of a physical environment that updates continuously with real-world data. AI enhances digital twins by enabling predictive modeling—allowing users to simulate different scenarios and plan for the future. For example, a city’s digital twin can predict the impact of new infrastructure projects on traffic congestion before they are even built.
Predictive Analytics & Time-Series Forecasting
AI-powered time-series forecasting uses past and present data to predict future changes. This is particularly useful for environmental applications, such as forecasting rising sea levels, tracking urban heat islands, or anticipating extreme weather events.
Applications of AI-Driven 4D Maps
The ability to visualize and predict how geographic spaces change over time has profound implications across multiple industries. Here are some of the most exciting applications of 4D mapping technology:
Urban Planning & Smart Cities
4D maps help city planners make data-driven decisions by analyzing trends in population growth, infrastructure development, and transportation networks. AI can forecast traffic congestion, optimize public transport routes, and improve overall city efficiency. Smart cities use this technology to ensure sustainable growth while minimizing environmental impact.
Environmental Monitoring & Climate Change
From tracking deforestation to monitoring ice cap melting, 4D maps are revolutionizing climate science. AI-driven models allow researchers to study long-term changes in ecosystems and predict the consequences of environmental shifts. Policymakers can use this data to implement conservation strategies and combat climate change effectively.
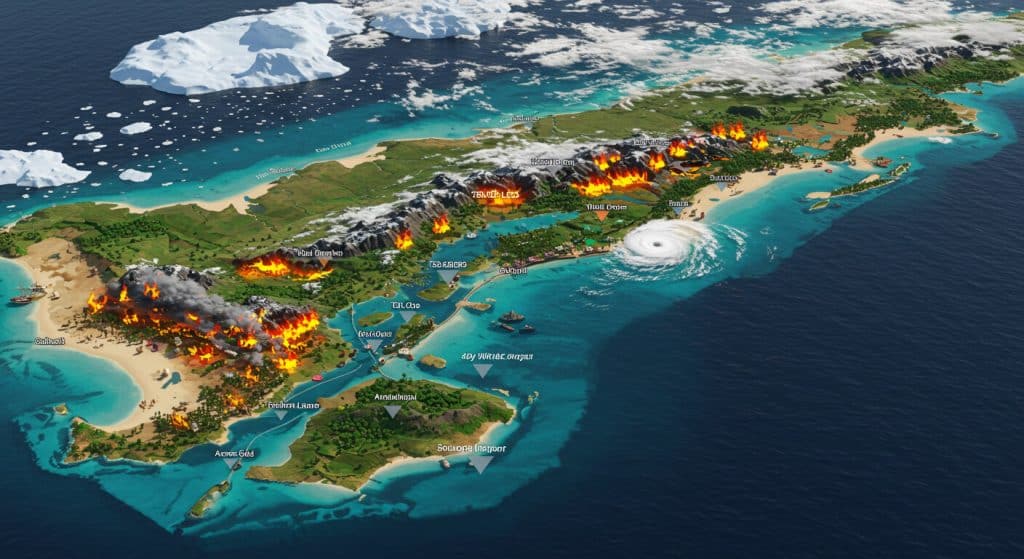
Disaster Management & Risk Assessment
When natural disasters strike, 4D maps provide real-time information that helps emergency responders allocate resources efficiently. AI can predict where a wildfire will spread next, analyze flood patterns, or assess earthquake risks by studying geological changes over time. This proactive approach can save lives and mitigate damage.
Transportation & Navigation
4D maps are set to transform transportation systems by optimizing routes based on historical traffic data, weather conditions, and urban expansion trends. AI-powered predictive navigation can suggest the fastest and safest routes, reducing congestion and fuel consumption.
Agriculture & Land Management
Farmers and agricultural scientists use 4D maps to analyze soil health, weather patterns, and crop cycles. AI can predict droughts, track pest infestations, and optimize irrigation strategies, leading to increased food production and sustainability.
The Technology Behind 4D Mapping

Several groundbreaking technologies are making AI-driven 4D mapping possible:
Voxel Mapping
This technique uses 3D pixels (voxels) to create detailed spatial models. By incorporating time, voxel-based mapping can generate accurate digital twins for urban planning and environmental analysis.
Google’s Immersive View
Google’s AI-driven immersive mapping feature merges billions of aerial and street-level images to create a rich, time-sensitive navigation experience.
GIS & Spatial AI
Geospatial Information Systems (GIS) combined with AI allow for the integration of various data sources, creating highly detailed and predictive 4D maps.
The Future of AI-Driven 4D Maps
As AI technology advances, the capabilities of 4D mapping will continue to grow. Future developments may include:
Real-Time 4D Mapping
The integration of AI with live data feeds from IoT sensors and autonomous drones will enable real-time 4D maps that update continuously.
Augmented Reality (AR) Integration
Users may soon be able to interact with 4D maps in AR environments, providing an immersive way to visualize spatial and temporal data.
Conclusion
The transition from 2D to 4D mapping marks a significant milestone in the evolution of geospatial technology. By incorporating AI, maps are no longer static representations of the world but dynamic, time-aware systems capable of tracking, analyzing, and predicting changes across landscapes, cities, and ecosystems.
Whether improving urban planning, mitigating climate change, or enhancing disaster response, AI-driven 4D maps are set to reshape how we interact with geographic data. As technology advances, the possibilities for time-based mapping will only expand, paving the way for smarter, more sustainable decision-making.


